Heatwave leading to ozone

Heatwaves can have a significant impact on air quality and can contribute to an increase in ozone pollution. Ozone pollution, often referred to as ground-level ozone or smog, occurs when there are high concentrations of ozone near the Earth's surface. This type of ozone is different from the ozone layer found in the upper atmosphere, which protects us from the sun's ultraviolet radiation.
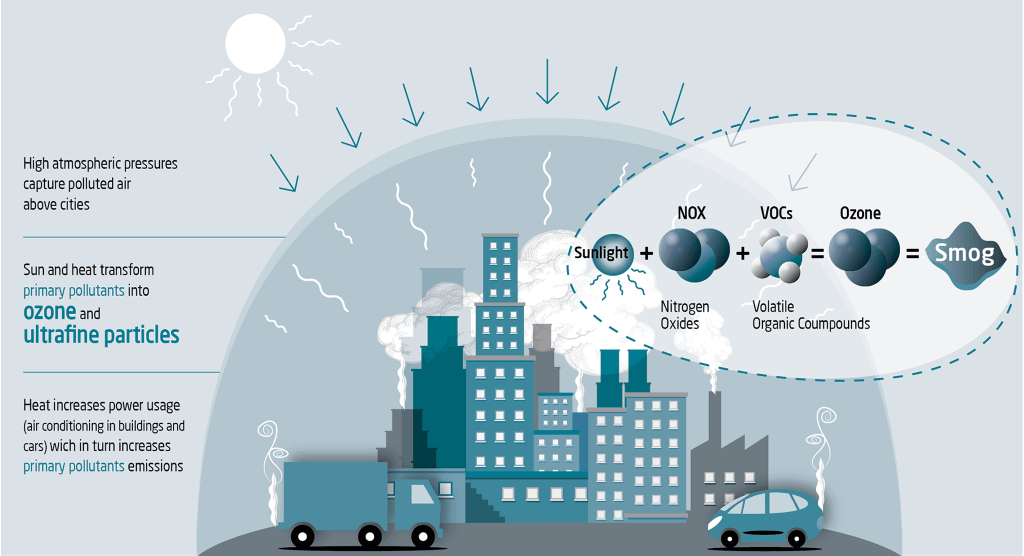
Here's how heatwaves can lead to ozone pollution:
1. **Chemical Reactions:** Heatwaves can elevate temperatures, which, in turn, increase the chemical reactions that produce ground-level ozone. Ozone is formed when volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and nitrogen oxides (NOx) react in the presence of sunlight. Higher temperatures can speed up these reactions, leading to higher ozone concentrations.
2. **Stagnant Air Masses:** During heatwaves, there is often a lack of air movement or stagnant air masses. This stagnant air traps pollutants closer to the surface, preventing them from dispersing into the atmosphere. As a result, ozone and other pollutants can accumulate, leading to poorer air quality.
3. **Increased Emissions:** Heatwaves can also lead to an increase in emissions of VOCs and NOx. For example, people tend to use more air conditioning and drive their cars more during hot weather, which can release additional pollutants into the air. Industrial processes and power plants may also run at higher capacities, emitting more pollutants.
4. **Natural Emissions:** Heatwaves can enhance natural emissions of VOCs from vegetation. Plants release VOCs, and these compounds can react with NOx to form ozone in the presence of sunlight. High temperatures can increase the rate of VOC emission from plants, contributing to ozone formation.
5. **Health Impact:** Ozone pollution is harmful to human health, particularly during heatwaves when people are more vulnerable to respiratory problems and heat-related illnesses. Prolonged exposure to high ozone levels can lead to breathing difficulties, exacerbate asthma and other respiratory conditions, and increase the risk of heat-related illnesses.
To mitigate the effects of heatwaves on ozone pollution, it's crucial to reduce emissions of VOCs and NOx from various sources, including vehicles, industrial facilities, and power plants. Additionally, public awareness and preparedness for heatwaves can help people take steps to reduce their personal contributions to ozone pollution, such as limiting outdoor activities during high ozone days and conserving energy to reduce emissions from power generation.